We endeavor to offer our customers exceptional support to ensure a delightful product experience.
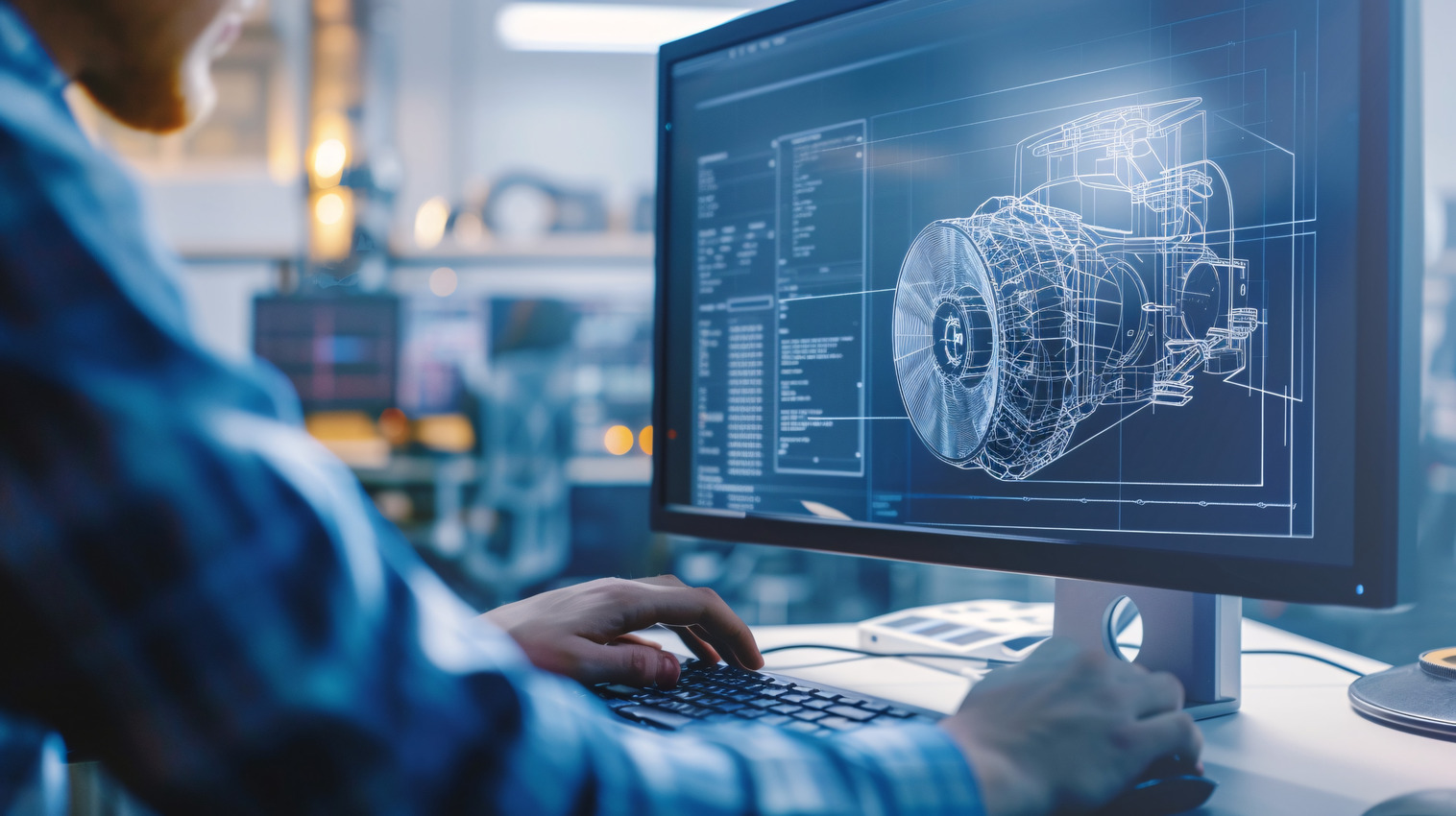


BIMDeX connects CAD, design, and BIM software, enabling seamless data exchange with its BXF toolkit and ML, ensuring no loss of geometry or metadata.

BIMDex is proud to partner with a global network of trusted resellers who help bring our innovative BIM solutions to businesses worldwide.


The experts and expertise are under one single roof of brilliance! Here is the Design and Make conference from Autodesk to empower everyone and everything to change trivia to a matter of fact.

What is essential for an industry, especially an industry like AEC? While we say there are various important aspects that sustain the industry, one prominent factor is a col
How would you test a car? On a test track, or on real roads? Many BIM managers make
The engineering and construction aspects, which were just a mere dream in the primitive times, have become the most inevitable factor of the industry in recent times, with t
A major practice that has grown highly inevitable in the construction and manufacturing industries is the use of different design data from vital software. A model and the d
In recent years, the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industries, and the major disciplines of Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP), have been seeing

Discover the latest updates, industry news, and insights from the world of CAD, BIM, and design technology.
Autodesk Partners with SrinSoft Inc. to Revolutionize Interoperability
Autodesk is excited to announce a partnership with APS certified partner SrinSoft Inc. This collaboration aims to address the interoperability challenges faced by the architecture, engine...
Convergence of Engineering Design & Data
Digital transformation begins with convergence, connecting your organization using data while bridging
Enterprise Connected Data Through Interoperability
Enterprise Interoperability is the ability of an enterprise - a company or other large organization—to functionally link activities,
BXF - Collaborate from a Single Source of Data
As part of our long-standing commitment to cross-platform interoperability, we continue to ensure that our portfolio of products meets the rigorous requirements of design

BIMDeX & DATA EXCHANGE (DX) INTEGRATION
CAD, DESIGN & BIM INDUSTRIES

Our team is ready to help


BIMDeX connects CAD, design, and BIM software, enabling seamless data exchange with its BXF toolkit and ML, ensuring no loss of geometry or metadata.
BIMDex is proud to partner with a global network of trusted resellers who help bring our innovative BIM solutions to businesses worldwide.
BIMDeX connects CAD, design, and BIM software, enabling seamless data exchange with its BXF toolkit and ML, ensuring no loss of geometry or metadata.
BIMDeX connects CAD, design, and BIM software, enabling seamless data exchange with its BXF toolkit and ML, ensuring no loss of geometry or metadata.

Experience the power of BIMDeX solutions.
Request a free demo now and see how it can benefit your business.


The experts and expertise are under one single roof of brilliance! Here is the Design and Make conference from Autodesk to empower everyone and everything to change trivia to a matter of fact.



What is essential for an industry, especially an industry like AEC? While we say there are various important aspects that sustain the industry, one prominent factor is a col
How would you test a car? On a test track, or on real roads? Many BIM managers make
The engineering and construction aspects, which were just a mere dream in the primitive times, have become the most inevitable factor of the industry in recent times, with t
A major practice that has grown highly inevitable in the construction and manufacturing industries is the use of different design data from vital software. A model and the d
In recent years, the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industries, and the major disciplines of Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP), have been seeing
Custom WGM on BIMDeX enables personalized workflows, automating BIM processes to streamline project execution and enhance team collaboration with flexible data handling.
CAD, DESIGN & BIM INDUSTRIES
The BIMDeX Manager from BIMDeX appears to work by managing and converting BIM data between different software platforms, ensuring smooth interoperability within the AEC industry.
Custom WGM on BIMDeX enables personalized workflows, automating BIM processes to streamline project execution and enhance team collaboration with flexible data handling.

Our team is ready to help


Discover the latest updates, industry news, and insights from the world of CAD, BIM, and design technology.
Autodesk Partners with SrinSoft Inc. to Revolutionize Interoperability
Autodesk is excited to announce a partnership with APS certified partner SrinSoft Inc. This collaboration aims to address the interoperability challenges faced by the architecture, engine...
Convergence of Engineering Design & Data
Digital transformation begins with convergence, connecting your organization using data while bridging
Enterprise Connected Data Through Interoperability
Enterprise Interoperability is the ability of an enterprise - a company or other large organization—to functionally link activities,
BXF - Collaborate from a Single Source of Data
As part of our long-standing commitment to cross-platform interoperability, we continue to ensure that our portfolio of products meets the rigorous requirements of design

We endeavor to offer our customers exceptional support to ensure a delightful product experience.